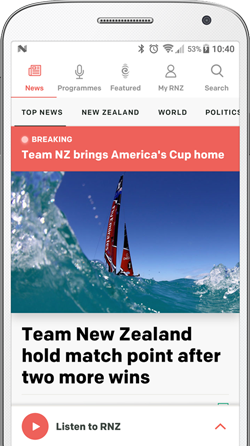
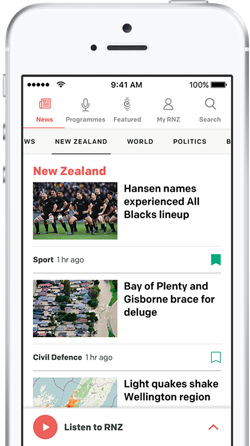
A view of the iron mine of Swedish state-owned mining company LKAB in Sweden’s northernmost city Kiruna. Photo: Jonas EKSTROMER / TT News Agency / AFP
Europe's largest deposit of rare earths - which are used from mobile phones to missiles - has been found in Sweden.
No rare earths are mined in Europe at the moment, and a Swedish minister hailed the find as a way of reducing the EU's dependence on China.
The discovery is also being seen as "decisive" for the green transition, given the expected rise in demand for electric vehicles and wind turbines.
Some 98 percent of rare earths used in the EU in 2021 were imported from China.
Over 1 million tonnes are reported to have now been found in Sweden's Far North.
Although significant, that is a fraction of the world's 120 million tonne reserves, according to a US estimate.
The term rare earth refers to a group of 17 elements that are used to make a range of products and infrastructure which are increasingly important to everyday life.
They can be found in mobiles, hard drives and trains. But they are also important for green technology including wind turbines and electric vehicles. Some are essential for military equipment like missile guidance systems.
Extraction is both difficult and potentially damaging to the environment.
Demand for them is expected to increase fivefold by 2030.
"Lithium and rare earths will soon be more important than oil and gas," the EU's internal market commissioner Thierry Breton said last year.
Speaking at a press conference on Thursday, Swedish Energy Minister Ebba Busch said the EU was "way too dependent on other countries for these materials" and insisted a change was needed.
"Electrification, the EU's self-sufficiency and independence from Russia and China will begin in the mine", she asserted.
The newly discovered raw materials may not reach the market before 10-15 years' time, the mining company's CEO Jan Mostrom said. Permitting processes take time due to environmental risk evaluations.
But Mostrom called on authorities to speed up the process, "to ensure increased mining of this type of raw material in Europe".
- BBC